Product Manager Role & Responsibilities
1. Understand the market
To develop successful products, a product manager needs a deep understanding of the market. Identifying and anticipating customer needs helps the team develop, position, and market the product more effectively. Understanding the broader market helps a product manager ensure the product remains relevant and competitive.
2. Develop the product vision
The product vision provides a clear picture of the product’s purpose, value proposition, and long-term objectives. This vision unifies stakeholders, executives, and product teams around the product’s direction. In addition, the product vision provides a strategic framework that informs decision-making throughout the product lifecycle, ensuring that each feature, enhancement, or pivot contributes to the overall success of the product.
3. Define the product strategy
The product strategy is a high-level plan that outlines the overarching goals, direction, and approach for the product. Essentially, it defines the “what” and the “why” of the product. To create a product strategy, a product manager typically researches market trends, customer pain points and preferences, and the strengths and weaknesses of competitors. The product manager then defines clear goals, objectives, and key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with the product vision.
4. Create the product roadmap
The product roadmap is a more detailed, tactical plan that breaks down the product strategy into actionable steps. It details the “how” and the “when” of product development. As with the product vision and strategy, the product roadmap helps various stakeholders, including executives, sales and marketing teams, and development teams, stay aligned. The roadmap is a living document, and the product manager will continuously update it as the product evolves.
5. Monitor performance
The overarching goal of performance monitoring is to determine if the product is meeting the goals identified in the product strategy. Performance monitoring also gives the product manager data to inform decision-making, planning, and cross-functional coaching. To monitor performance, a product manager will first identify key success metrics and set up tracking tools. The product manager will review and analyze metrics regularly in order to iteratively improve the product.
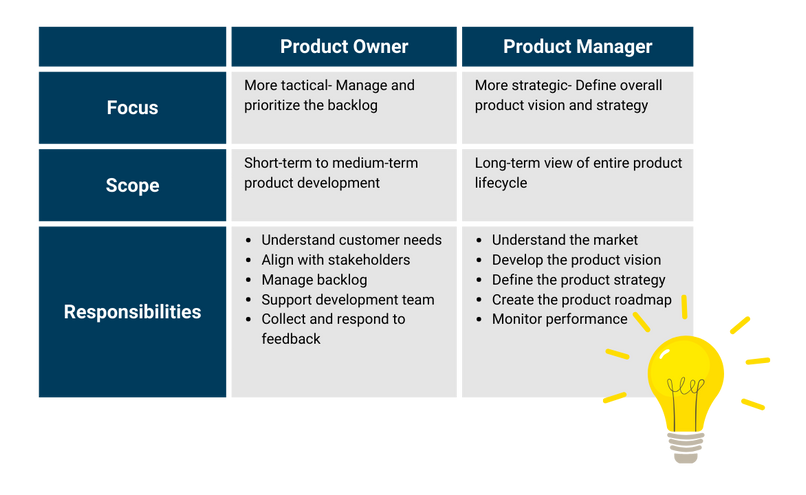
Can a Product Owner Also Be a Product Manager?
In some organizations, especially in smaller companies, a single person may take on both the product owner and product manager roles.
In such cases, the individual must balance both the tactical aspects of managing the product development process (product owner role) and the strategic aspects of product planning (product manager role).
Do Organizations Need Both Roles?
The need for both product owners and product managers in an organization depends on various factors, including the size and complexity of the product and the organization's structure. In most cases, having both roles will benefit large organizations or products with complex development and market considerations.
In conclusion, the differences between a product owner and a product manager can be subtle, but both are integral to the success of a product. Together, these two roles can unlock innovation that will set products apart from the competition.
Want to learn more about product ownership or product management? Consider taking an ICAgile certification class. Developed by leaders in the field and focused on industry best practices, ICAgile's certifications give you knowledge and skills to help advance your career.